How to Replace an A/C Compressor!!!

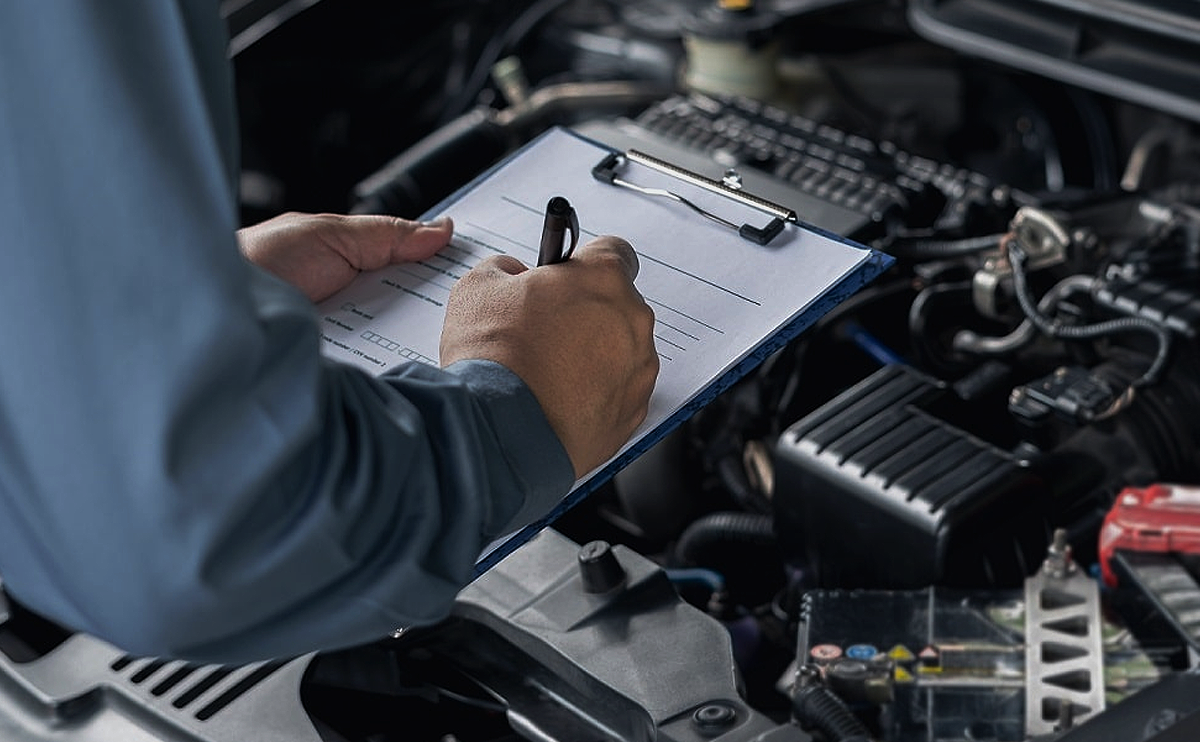
Summertime driving is made much more pleasant with cold air blowing from your vents. But if it’s not getting as cold as it used to or the air isn’t giving you any reprieve from the heat, your A/C compressor could be to blame. It’s one of the critical parts to make the system work, and driving in hot weather will become sweltering if it has failed.
Changing the A/C compressor can be a big job, and parts are usually an average of $375 plus seals, refrigerant, and related items. But the compressor itself can range from around $200 to more than $2,000. It’s a job that takes some planning, but the bulk of the work can be done at home if you have a well-stocked garage.
Learn more about the process of how to replace an A/C compressor along with common issues, limitations, and what it takes to do the job.
Introduction to A/C Compressor Replacement
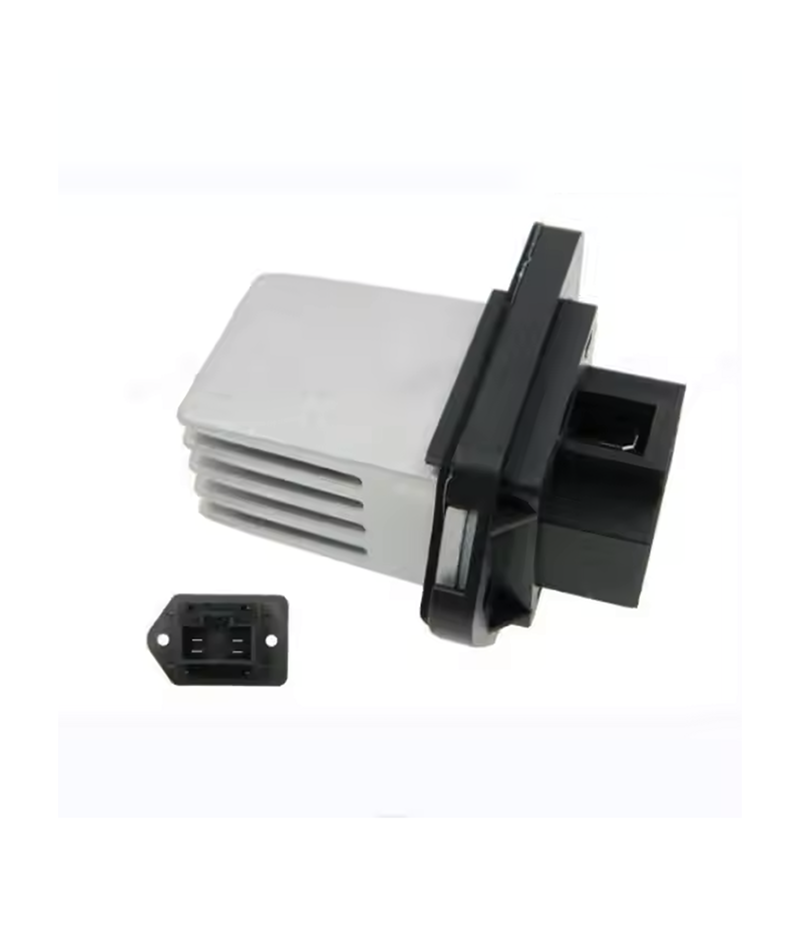
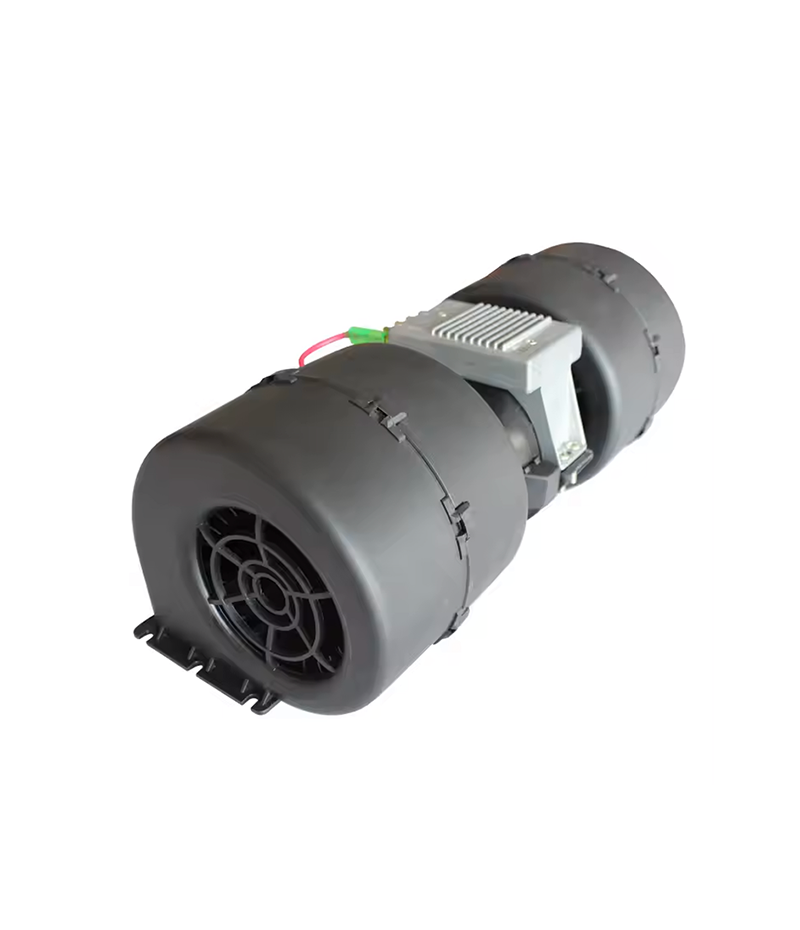
The air conditioning compressor, or A/C compressor, serves as the heart of your vehicle’s air conditioning system, playing a crucial role in cooling your car. It functions by circulating refrigerant necessary for heat exchange through the coils of the cabin’s evaporator and the condenser in the engine bay.
The A/C compressor operates on a simple principle: it compresses the refrigerant gas, raising its temperature and pressure, and sends it through the system’s condenser where it becomes a cool, low-pressure liquid. It then passes into the cabin where a fan blows over the cold evaporator, cooling the interior air while absorbing heat to move out of the cabin. This process is vital in keeping the interior of your car comfortable during hot weather.
However, just like any other component in your vehicle, the A/C compressor can wear out over time due to factors such as age, mileage, or mechanical failure. When this happens, it’s unable to perform its job effectively, leading to a less effective A/C system or even complete failure.
In such cases, replacing the A/C compressor becomes necessary to restore the cooling efficiency of your car to ensure not only your comfort but also your vehicle’s A/C system performance.
Related: How Much Does it Cost to Replace Your Car’s AC?
Necessary Tools and Safety Precautions
Changing an A/C compressor requires a specific set of tools. Here’s a list of what you might need:
- Wrenches and sockets for removing and attaching bolts.
- Screwdrivers for various parts of the process.
- Pliers for removing clips or clamps.
- A/C manifold gauge set to monitor the pressure of the A/C system.
- Refrigerant recovery machine that safely removes existing refrigerant from the system.
- Vacuum pump to remove any air and moisture from the system.
- Safety glasses and gloves to protect your hands and eyes.
Related: Symptoms Of A Bad AC Compressor
As for safety precautions:
- Always wear safety glasses and gloves to protect yourself from injury.
- Never release refrigerant into the atmosphere. It’s not only harmful to the environment but also illegal in many places. Use a refrigerant recovery machine to safely handle it.
- Be careful when working with the vehicle’s electrical system. Disconnect the battery before starting work to avoid shocks.
- Ensure the vehicle is securely parked and cannot move or roll while you’re working on it.
- Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions when installing the new compressor to ensure proper installation and operation.
It’s not feasible to have a refrigerant recovery machine or a vacuum pump on hand in your garage unless you’re a professional mechanic. So, consider having the system evacuated by your preferred shop before starting the repair, then have them recharge the system afterward too.
Related: How to Recharge Your Car’s AC System
Step-by-Step Guide to Replacing an A/C Compressor
Again, unless the system is empty, don’t begin disassembling any parts that could release the refrigerant into the atmosphere. But once a mechanic has evacuated the system, it’s safe to get started. Each vehicle has a nuanced process, but these are the general steps.
- Step 1: Remove the compressor belt. Locate the compressor belt on the front of the compressor and remove it. You may need to loosen other belts to access it.
- Step 2: Disconnect the electrical connector. Find the electrical connector on the compressor – it should have a wire leading into it. Then, carefully unplug it.
- Step 3: Disconnect the refrigerant lines. Using your wrenches, disconnect the refrigerant lines from the compressor. Remember to cap these lines to prevent contaminants from entering the system.
- Step 4: Remove the compressor. Now, you can remove the bolts that hold the compressor in place. Make sure to keep track of all bolts and where they came from for easier reassembly. Carefully lift the compressor out of the vehicle.
- Step 5: Install the new compressor. Place the new compressor in the same position as the old one. Reattach the bolts, connect the refrigerant lines, plug in the electrical connector, and reattach the compressor belt. Use new seals at each of the connections to avoid leaks.
With the system assembled, get your mechanic to vacuum test, recharge the system, with refrigerant, and confirm that it’s operational.
Related: How To Fix AC In Car
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Replacing an A/C compressor can come with a few common issues, and knowing how to handle these can make the process smoother. Here are some of those issues and their solutions:
- Insufficient cooling. After replacing the compressor, the A/C might not cool the car as expected. This could be due to improper vacuuming before recharging the refrigerant or a leak in the system. The solution is to check for leaks and ensure the system is properly vacuumed and recharged.
- Compressor clutch not engaging. If the compressor clutch doesn’t engage, it could be due to electrical issues or a faulty clutch. Check the wiring and fuses, and if they’re fine, the clutch might need to be replaced.
- Noises after installation. Unusual noise after installation could indicate that the compressor was not installed correctly or there are loose mounting bolts. Recheck the installation and make sure all bolts are tightened correctly.
- Refrigerant leaks. This could be due to damaged seals or improper connections to the refrigerant lines. Inspect all seals and connections, and replace or tighten them as necessary.
- Electrical issues. If the compressor isn’t getting power, the problem could be with the wiring, fuses, or relay. A thorough inspection of the electrical components can help identify and resolve the issue.
Always remember, if you’re unsure about any part of the process, it’s best to consult with a professional to avoid damaging your vehicle or hurting yourself.
Related: Automotive Heating
Potential Drawbacks and Limitations
It’s not always advised to do the job yourself. With an A/C compressor, it’s precision work that could go sideways quickly.
If a seal falls out, gets nicked or cut, or gets reused instead of replaced, it can cause a leak that depletes the refrigerant over the course of days, weeks, or months. As well, if dirt and other contaminants get into the system while you’re working on it, other parts can fail too. Plus, you might discover that there are other issues contributing to poor A/C performance, and the A/C might still not blow as cold as it once did.
Since refrigerant is strictly regulated, it’s a job that still can’t be fully done – at least, not legally – without a certified technician dealing with evacuating and recharging it. If you decide that it’s too big a job to tackle on your own, let AutoZone help you find qualified professional mechanics through our Shop Referral Program.
And whether you’re working on it yourself or bringing parts to a professional, find your new A/C compressor at your local AutoZone. Shop today to explore parts from trusted brands, designed to work specifically for your vehicle.